Epilepsy, Types, causes, symptoms, Remedies & Cure
What Is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterised by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. Seizures occur when there is a sudden, abnormal electrical activity in the brain, which can cause a variety of symptoms depending on the part of the brain affected.Epilepsy can develop at any age, but it often begins in childhood or adolescence. Diagnosis of epilepsy typically involves a neurological exam, medical history, and various tests, such as electroencephalogram (EEG) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Living with epilepsy can be challenging, and it may require lifestyle modifications to manage the condition effectively.It's important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalised treatment plan and manage any potential complications of the condition.
Epilepsy Symptoms
The symptoms of epilepsy can vary depending on the type of seizure and the part of the brain affected. Some common symptoms of epilepsy may include:
-
Convulsions or uncontrolled movements of the arms and legs
-
Staring spells or sudden loss of consciousness
-
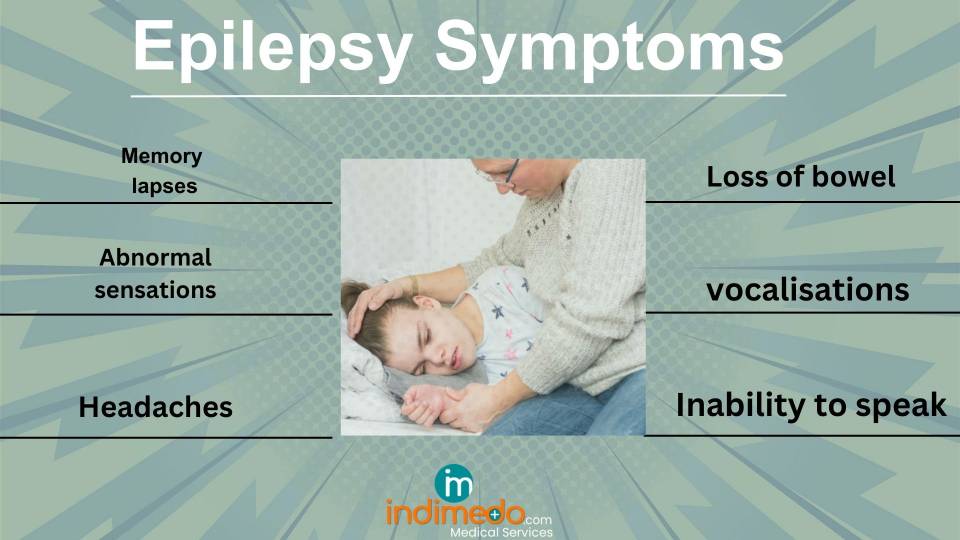
Confusion, disorientation, or memory lapses
-
Abnormal sensations, such as tingling, numbness, or "electric shock" sensations
-
Changes in mood or behaviour, such as sudden aggression or euphoria
-
Inability to speak or understand language
-
Repetitive movements or vocalisations
-
Loss of bowel or bladder control
-
Headaches or migraines
Some seizures can occur due to other medical conditions, such as a high fever, low blood sugar, or alcohol withdrawal.
Types Of Epilepsy
There are several types of epilepsy, each of which is characterised by different types of seizures and patterns of electrical activity in the brain. Here are some of the most common types of epilepsy:
-
Idiopathic generalised epilepsy: This type of epilepsy often begins in childhood or adolescence and is believed to have a genetic basis. It is characterised by seizures that involve both sides of the brain and often cause convulsions or loss of consciousness.
-
Temporal lobe epilepsy: This type of epilepsy is characterised by seizures that originate in the temporal lobes of the brain, which can cause symptoms such as altered emotions or sensations, visual or auditory hallucinations, and loss of awareness.
-
Frontal lobe epilepsy: This type of epilepsy is characterised by seizures that originate in the frontal lobes of the brain and may cause symptoms such as sudden movements or vocalisations, altered behaviour or mood, and loss of awareness.
-
Occipital lobe epilepsy: This type of epilepsy is characterised by seizures that originate in the occipital lobes of the brain and can cause visual disturbances such as flashes of light or distorted vision.
-
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: This type of epilepsy often begins in adolescence and is characterised by seizures that involve sudden, brief muscle jerks, particularly in the arms and shoulders.
-
Benign rolandic epilepsy: This type of epilepsy is most commonly seen in children and is characterised by seizures that originate in the rolandic area of the brain, which can cause tingling or numbness in the face or tongue, and may also cause convulsions.
What Causes Epilepsy?
The exact causes of epilepsy are not always known, but there are a number of factors that can contribute to its development. Here are some of the most common causes of epilepsy:
-
Brain injury: Any type of brain injury, such as a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or infection, can increase the risk of developing epilepsy.
-
Genetics: There may be a genetic component to epilepsy, as it often runs in families. Some specific genes have been identified that are associated with an increased risk of developing epilepsy.
-
Brain malformations: Some individuals may be born with structural abnormalities in their brains that can lead to seizures and epilepsy.
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and brain abscesses, can cause inflammation in the brain that can lead to seizures and epilepsy.
-
Developmental disorders: Conditions such as autism spectrum disorder or neurofibromatosis can increase the risk of developing epilepsy.
-
Brain tumours: Tumours in the brain can disrupt normal brain function and lead to seizures and epilepsy.
-
Substance abuse: Substance abuse, particularly of alcohol or cocaine, can increase the risk of developing epilepsy.
Natural Remedies For Epilepsy
While there are medications and other treatments available to manage epilepsy, some individuals may also be interested in exploring natural remedies. It's important to note that natural remedies should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment, and individuals should always consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment. Here are some natural remedies that may be helpful for managing epilepsy:
-
Ketogenic diet: The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has been shown to be effective in reducing seizures in some individuals with epilepsy.
-
Yoga and meditation: Some individuals with epilepsy have found that practices such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which may in turn help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
-
Essential oils: Certain essential oils, such as lavender, chamomile, and frankincense, may have calming and soothing properties that can help reduce stress and anxiety, which may in turn help reduce the frequency of seizures.
-
Acupuncture: Acupuncture is an ancient practice that involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body. Some individuals with epilepsy have found that acupuncture can help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
-
Herbal supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as ginkgo biloba and valerian root, have been suggested to have anti-seizure properties. However, it's important to note that the safety and efficacy of these supplements have not been well-studied, and they should not be used without consulting a healthcare professional.
Epilepsy Cure
Currently, there is no known cure for epilepsy. However, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the condition and reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Medications are often the first line of treatment for epilepsy. There are many different types of anti-seizure medications available, and the choice of medication will depend on the type of epilepsy a person has and other individual factors.
In addition to medication, other treatments that may be effective for managing epilepsy include:
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the part of the brain that is causing seizures.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): VNS involves the implantation of a device that stimulates the vagus nerve in the neck, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
-
Responsive neurostimulation (RNS): RNS involves the implantation of a device in the brain that detects and responds to seizure activity.
-
Ketogenic diet: As mentioned earlier, the ketogenic diet has been shown to be effective in reducing seizures in some individuals with epilepsy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, epilepsy is a neurological disorder that is characterised by seizures. While the exact causes of epilepsy are not always known, there are a variety of factors that can contribute to its development, including brain injury, genetics, and brain malformations. While there is no known cure for epilepsy, there are many treatments available to help manage the condition and reduce the frequency and severity of seizures, including medication, surgery, and alternative therapies such as the ketogenic diet and acupuncture. It's important for individuals with epilepsy to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that works best for them, and to always prioritise safety and proper medical care.





 Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook
 Login with Google
Login with Google